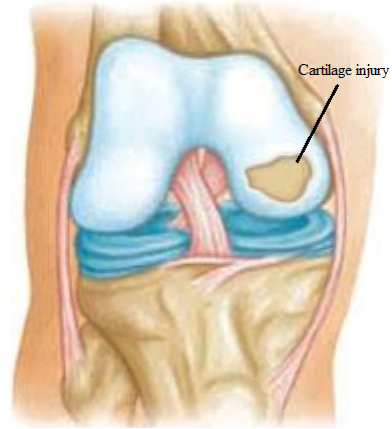
Knee joint showing focal cartilage damage
Overview of Articular Cartilage Injury (knee)
Articular Cartilage is connective tissue not hard as bone but firm enough to absorb stresses placed on bones, so act like a “shock absorber”. Articular Cartilage also provides smooth gliding surfaces to reduce friction. Articular Cartilage covers ends of shin bone, thigh bone and under surface of knee cap.
Injury can happen due to
- Trauma- direct impact or twisting of leg when the knee is bent.
- Sports injury- repetitive micro traumaduring sports activity.
- aging process (degeneration) Superficial damage or softening of cartilage is called Chondromalacia, a mild form Osteoarthritis. Injury to cartilage could be just softening to partial or complete separation of flap of cartilage with exposed underlying bone. When separated completely from bone then it will form“ loose body” inside the knee joint.
- Constant dull pain more with climbing stairs or getting up from sitting.
- swelling.
- Painful movements.
- Mechanical symptoms of locking or catching in case of loose body.
Are you an athlete who has sustained knee articular cartilage injury?
You can consult Dr. Abhijit Ranaware (Knee and sports injury Specialist)
Book Appointment by Filling Form Below:
How to know if you are suffering from Cartilage injury?
Dr. Abhijit Ranaware will ask for history of traumatic event & examine knee with feeling for tenderness at site of cartilage damage. He will also do specific test & feel for any loose body – “joint mouse”. Dr. Abhijit Ranaware may advise following investigations in suspected knee cartilage injury.
X-rays – to see for any knee arthritis associated with joint alignment.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI scan) – to confirm severity and depth of cartilage injury. 3 Tesla MRI with high quality imaging would give better cartilage mapping and help in planning further treatment.

