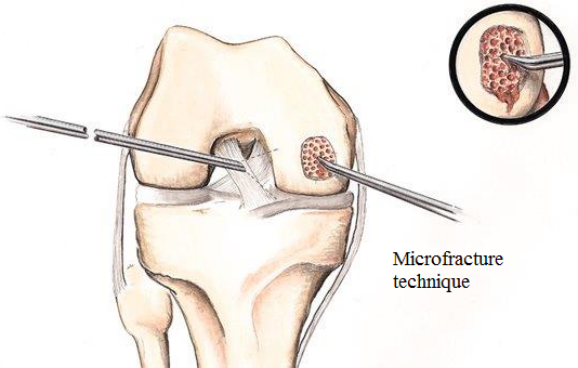
Microfracture- Holes made in cartilage defect with fine pointed instrument
Treatment of Articular Cartilage Injury (knee)
Knee joint is largest joint in body and most prone to get articular cartilage injury. Sometimes cartilage damage is associated with other knee ligament or meniscal injury. Treatment of cartilage injury depends on location and size of cartilage damage. Superficial damage or softening of cartilage is called Chondromalacia, a mild for Osteoarthritis.
Immediately after any sports related injury, treatment follows RICE protocol, RICE stands for :
- Rest – in the form of knee brace to restrict knee movement and weight bearing
- Ice application
- Compression – with elastic crepe bandage
- Elevation - of leg above heart level with pillow beneath legs to prevent additional swelling.
Further treatment for small cartilage flap with superficial lesion would be mostly conservative. Treatment is focused on low-impact strengthening exercises mainly quadriceps muscles, to avoid stress on knee cartilage. If associated with irritation of joint capsule (Synovitis) a steroid injection may help to reduced inflammation. Role of PRP injection or Hyaluronic acid (visscosuplementation) is still remains unproven in cartilage injury. Since Cartilage lacks blood supply, healing is slow. Cartilage lesions on lower end of thigh bone (femur) are easier to treat with better results than on upper end of shin bone or under surface of knee cap (patella). Following are the surgical treatment options depending on location, size and depth of cartilage lesion done with arthroscopic (key hole) or minimally invasive open surgery. Chondroplasty: - Debridement, shaving-off the shredded superficial cartilage flap to reduce irritation and friction / repeated trapping between bony ends. Microfracture : when lesion is with the exposed bone and of small in size. Microfracture rely on patients own stem cells to form fibrocartilage. Simple arthroscopic procedure involves making holes in bed of cartilage to stimulate migration of bone marrow cell into the defect and form neocartilage.
Small piece of cartilage tissue is removed as like biopsy and sent to laboratory. The cartilage cells are fostered from biopsy tissue. After 6 weeks the newly formed millions of cartilage cells are implanted into the cartilage defect. The cells has potential to form new and healthy articular cartilage.
Allograft transfer:
Allograft transfer is to replace cartilage bone unit procured from donor. This procedure is done when large area of cartilage and underlying bone is damaged.
Biologics:
PRP or Stem cells are used as adjunct with cartilage transfer or repair for better healing.
Dr. Abhijit Ranaware, Knee and Sports Surgeon in Pune is highly experienced to treat knee articular cartilage injury with minimally invasive surgery technique and helps athletes to returning back to sports activity.
Post-op Rehab:
After surgery patient is suggested to apply ice and medications for few days. It is suggested to avoid putting weight on lower extremity and do machine assisted-continuous knee movement (CPM) for better cartilage healing.
Patient is discharged from hospital on the immediate next day and advised to undergo supervised. Physiotherapy sessions as per articular surgery rehab program.
Are you an athlete and want to know treatment options for articular cartilage injury?
You can consult Dr. Abhijit Ranaware (Knee and sports injury Specialist)
Book Appointment by Filling Form Below:
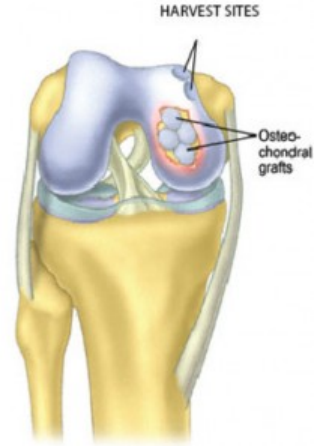
Osteochondral Autograft Transfer (OATs)
Osteochondral Autograft Transfer (OATs) – When the underlying bone is damaged in wider area then the cartilage defect filled with cylindrical bone plugs with attached cartilage cap from another non import portion of knee and press fitted into the cartilage void.